Principally, I'm interested in the computational modeling of linguistic theory.
I work at the University of Arizona (UA).
I direct and teach in the in-person Master's Program in Human Language Technology (HLT)
for the Department of Linguistics.
I'm also a member of the UA Cognitive Science Program and SLAT.
I have a long-term collaboration with linguistics faculty at Osaka Kyoiku University (OKU) in Japan.
I work primarily with professors Jason Ginsburg and Hiroshi Terada.
(Our universities have a formal academic exchange agreement.)

AI doesn't model human language. Bolhuis, Crain, Fong
and Moro.
Nature. Vol 627. 21 March 2024. pg. 489.
A letter to Nature.
 |
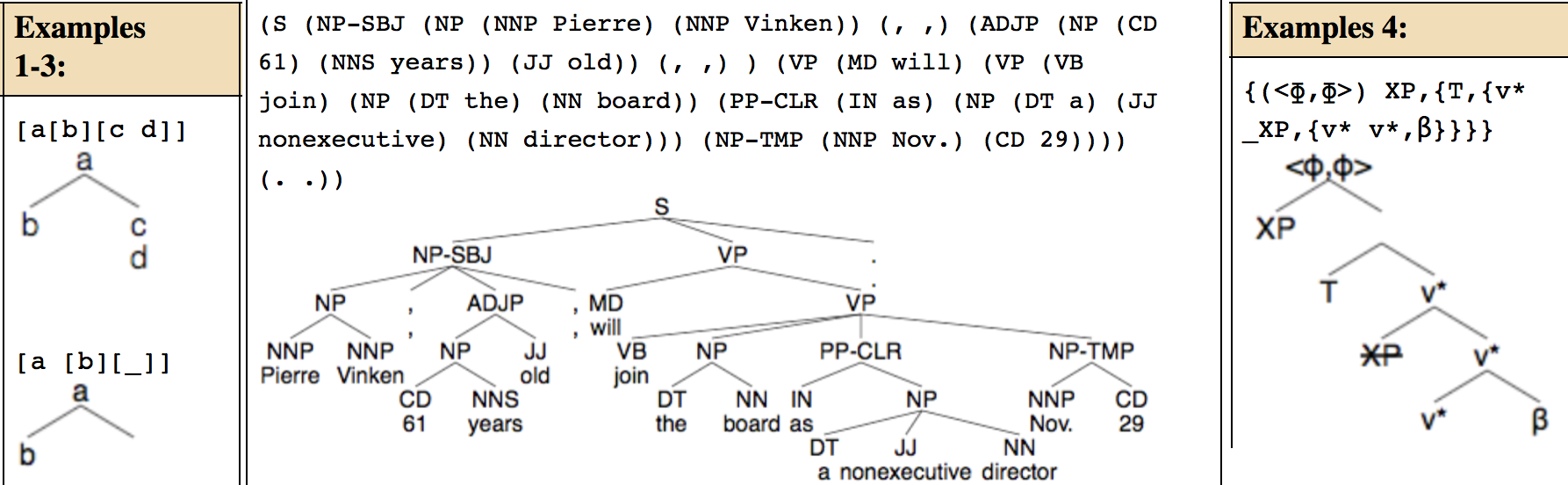
On the nature of FormSet.
Fong, S. & M. Oishi. Invited talk: Keio University, Feb 28-29 2024. Expanded talk slides: here |
Also
Abstract
Fong, S. & M. Oishi.
FIND-Workshop 2023. December 11-12. Göttingen, Germany.
Talk slides: here

|
Merge and the Strong Minimalist Thesis.
Chomsky, N., T. Daniel Seely, Robert C. Berwick, Sandiway Fong, M.A.C. Huybregts, Hisatsugu Kitahara, Andrew McInnerney, and Yushi Sugimoto. Cambridge University Press. Free download! link |
On the computational modeling of English relative
clauses.
Fong, S. & J. Ginsburg. (October 2023)
Open Linguistics, vol. 9, no. 1, 2023. Article number:
20220246, De Gruyter Open Access.
Link.
(Please download the PDF, not the HTML version that contains some errors.)
The Strong Minimalist Thesis (SMT): Form Copy (FC) and the
Serial Verb Construction (SVC).
Fong, S., J. Ginsburg,
M. Matsumoto & H. Terada.
In Proceedings of Japanese/Korean
Linguistics 30 (JK30). March 11th–13th 2023.
Simon
Fraser University, BC, Canada, pp.411-421, CSLI.
Link
Project: Minimalist Machine: computer implementation of
a generative theory in the Minimalist Program (MP).
See theory implemented and many examples of derivations.
(Joint work with Jason Ginsburg of Osaka Kyoiku University.)
Parsing with Box theory: to be updated soon.
Linguistic Theory and Deep Learning: On Generative AI
Even deeper problems with neural network models of
language. Thomas G. Bever, Noam Chomsky, Sandiway Fong and
Massimo Piattelli-Palmarini. Cambridge University Press. Dec 6th
2023. link
Data Connects Us: link
ChatGPT and Natural Language Understanding
Miscellaneous software projects. See also the Research tab for bigger software projects.
Homepages for classes that I teach are listed below.

Each Fall semester, I teach the gateway HLT core course, LING/C SC/PSYC 438/538 Computational Linguistics. There are no pre-requisites for graduate students, and it is open to anyone across the UA campus; however, priority for registration is given to Linguistics students. Auditors are also welcome. Although I teach programming from scratch in 438/538, some exposure/familiarity is normally advised. (Non-engineering undergrads or non-computer science undergrads without computational background are advised to take LING 388 Computers and Language first.) In Spring, I teach the follow-on core course to 438/538, this is LING/C SC/PSYC 582 Advanced Computational Linguistics. (Undergrads may take 582 with permission of instructor.) HLT students should take these two classes, 538 and 582, in order, and also take LING 439/539 Statistical NLP from another instructor in Spring following 538 in Fall.
Course webpages:- LING/C SC/PSYC 438/538 Computational Linguistics: Fall 2023
- LING/C SC/PSYC 408/508 Computational Techniques for Linguists: Fall 2023
- LING/C SC 581 Advanced Computational Linguistics: Spring 2024
- LING 388 Computers and Language Spring 2024
- Outreach talks.

(Example: at Basis Tucson North in 2019.)As part of the UA Department of Linguistics outreach, I sometimes give introductory talks aimed at high schoolers.
Once or twice a year, I also give more advanced introductory talks to undergrads at OKU.

- I sometimes serve as the faculty adviser for the UA Table Tennis Club.

(That's Dimitrij Ovtcharov at the LA Open in 2013.)I used to be an avid table tennis player, penhold style, but don't have much time to practice now, just play now and then on my table at home, see video clip here.
I know it's a bit of a promissory note, but some day in the future, I hope to seriously get back into this rather difficult, but cool sport.

|
I'm still an avid cyclist, though these days it's mostly about commuting and one weekend ride a week. I currently ride a range of different pedal-powered machines with different wheelsizes (ETRTO standards given here), which means I have to stock a lot of different tires and tubes. (Picture is from the 2005 edition of El Tour de Tucson. In the Platinum group. I'm on my custom Litespeed Ghisallo (ETRTO: 571mm, aka 650c), a relic from my Boston-Montreal-Boston randonee days. I think I ruined the handling of the bike when I installed a Look HSC fork in place of the rigid Alpha-Q fork.) |
Other machines:
- a blue Bike Friday Pocket Rocket Pro (ETRTO: 451mm, aka 20"). It's a folding travel bike that fits in a standard suitcase. Heavy and flexy, but it's very useful to have around, some pictures here.
- a modern Fuji carbon (ETRTO: 622mm, aka 700c). Strictly speaking, it's not my bike, but I find myself preferring it sometimes because the BB is so rigid and it has disc brakes.
- I also have a da Vinci tandem (with independent coasting).
- a low-racer recumbent (which I don't ride anymore as it has no suspension and is way slower than the vehicles mentioned below).
-
Most recently, I've acquired two velomobiles, a primary
and a backup. These are like tadpole trikes,
i.e. recumbent seating with two
wheels in front and a drive wheel in the back.
But velomobiles have a carbon-fiber fairing for extreme
aerodynamic efficiency. The best ones are of monocoque
construction and have no "frame".
The primary one is a Snoek (Dutch for pike) from velomobiel.nl. The backup is a DF from InterCity Bike. Both companies are based in Dronten, NL.
I currently commute using a velomobile (21 miles - 34 km - each way) using The Loop, accessing the Loop via either Mountain Ave or 6th Street/St. Mary's Rd from the campus.

|
For some weird reason, I enjoy running marathons (probably as an indicator of basic/everyday fitness). I started on this lark by training with the UA Running Club around campus several nights a week after work. I don't run with them anymore as I got too slow. I'm clearly no good at marathons, but I'm stubborn and have some endurance, so I finish. Last one I ran was back in 2019. Ideally, I'd like to run one a year. |
Osaka, Japan
It was in December, and I think caught the flu in Osaka beforehand. So I was feeling miserable. I thought I was going to start (大阪城 was near the hotel where I was staying at the time) and simply run until I saw the first subway station, but somehow I made it to the finish line.

(Finisher's medal.) |

(Osaka Castle at the start.) |
I'm also into making coffee ...